In order for your computer to store and manage specific files on your hard drive, it needs to create a partition or region of space to place information. If you’ve been looking around in your Windows Disk Management screen, you’ll notice that you have an EFI system partition which is (hopefully) listed as healthy. This is simply a division of your hard disk drive that was created during the installation of your operating system. It has several uses, and it can be deleted if you need to free up some space, but we recommend taking caution if you are planning to do so.
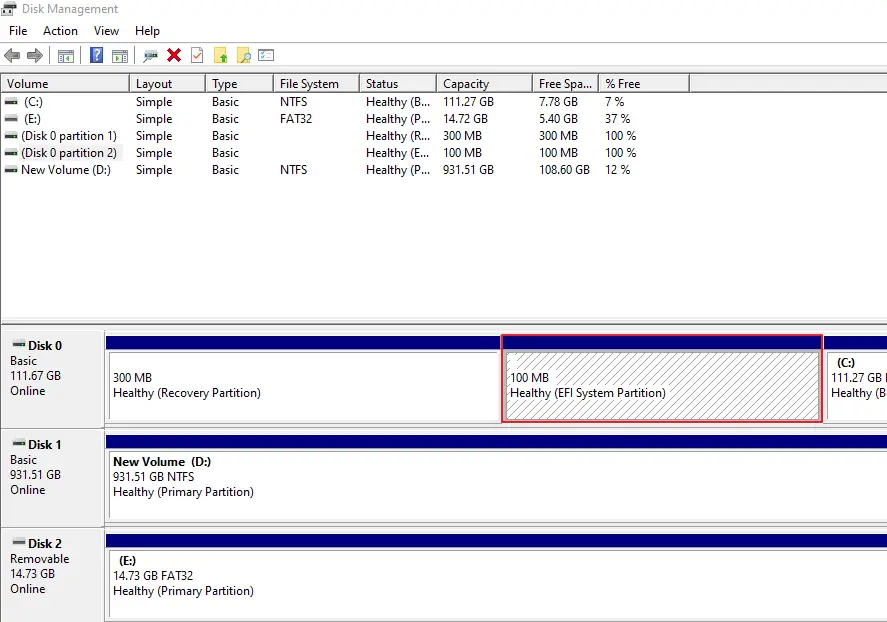
What is the EFI System Partition?
An EFI system partition is a region of space on your data storage device (hard disk drive) that is used by your Windows computer to adhere to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. Essentially, the EFI partition connects the operating system to the firmware of all hardware components on your computer. It is generated when you install the Windows operating system, and is used when the computer is turned on to boot the operating system and all necessary utilities. It consists of:
- The boot loaders needed to start the boot process. This includes system utilities, and device drivers.
- It contains all device drivers which is what tells Windows how to communicate with your hardware components (power supply, graphics card, central-processing unit, and more).
- It contains data files that hold all information needed about the boot process and any related logs.
- It runs small system utility programs that help start and run Windows on the initial boot up.
If you are using BitLocker to encrypt your hard drive, the BitLocker data that must interact with the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is also stored here.
Can you delete the EFI System Partition?
A lot of Windows users who are looking to free up additional space on their computer, may see the extra 100 MB of space that the EFI system partition is taking up and wonder if they can just delete the partition. While the answer is yes, you can delete it, it’s not necessarily a good idea.
You should not delete the EFI System Partition from a bootable drive
When you press the power button on your computer, Windows itself does not boot right away. Instead, the BIOS found on your motherboard boots first, and wakes up the hardware (physical devices), and firmware (software) on your computer. The BIOS will then look to the EFI system partition to get the instructions on how to boot up your Windows operating system.
If you go ahead and delete the EFI system partition, your motherboard’s BIOS is going to think that Windows does not exist on your computer, and thus your PC will not be able to boot Windows. This makes your system unbootable, and your computer essentially useless, which is why the EFI system partition is protected and locked to avoid accidental deletion. This is also why the EFI partition is not found in Windows File Explorer and why the delete button in the Disk Management screen is greyed out.
When should you consider deleting the EFI System Partition?
There are very few reasons why you would want to delete an EFI partition. The most common reason given is to remove it off of an external hard drive. This often happens when swapping out hard drives for larger ones, or if you plan on moving your operating system over to another hard drive.
The second reason is if you have an Apple Mac computer, and you are swapping the operating system for a Windows operating system. However, it’s a lot easier to just dual-boot instead.
Before you delete your EFI System Partition
Warning: If you are really keen on deleting your EFI system partition, please create a system backup or have a Windows 10 installation media disk nearby that you can use to restore your operating system. When deleting an EFI partition, things can go seriously wrong and cause your computer to become unbootable. If this happens, you will need to do a fresh installation or repair of your operating system.
Can you delete the EFI System Partition using the Disk Management tool?
No, you cannot delete the EFI system partition from the Disk Management screen. While Disk Management is an incredibly powerful built-in Windows tool, the EFI partition is going to be locked and protected, ensuring that the ability to delete it is disabled. If you go into your Disk Management screen and right-click on your EFI partition, you are going to see a completely greyed out menu.

If you right-click on any other partition, you’ll see that the menu is not greyed out.
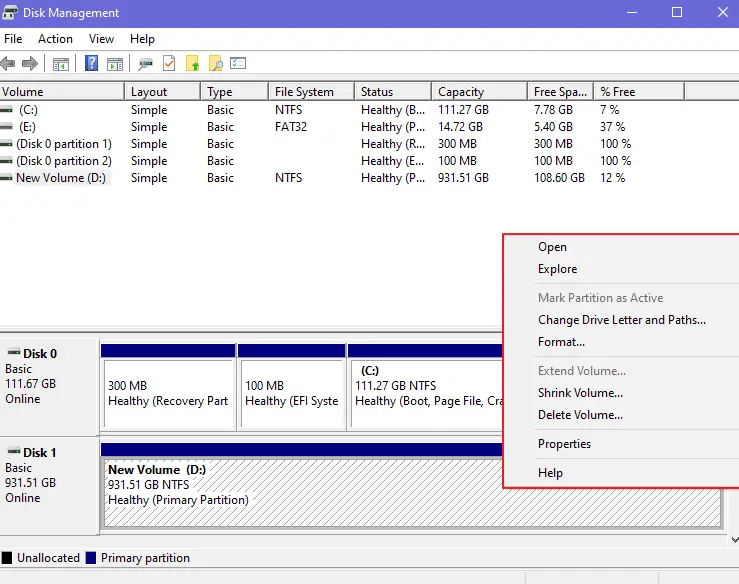
So, how do you delete an EFI system partition then?
How to delete the EFI System Partition using the DISKPART utility
DISKPART is a command-line tool that is used with the Command Prompt application on your Windows computer. Here is how to delete your EFI system partition using DISKPART:
- In your computer’s search menu, type in “CMD” or “Command Prompt“.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and click “Run as administrator“.

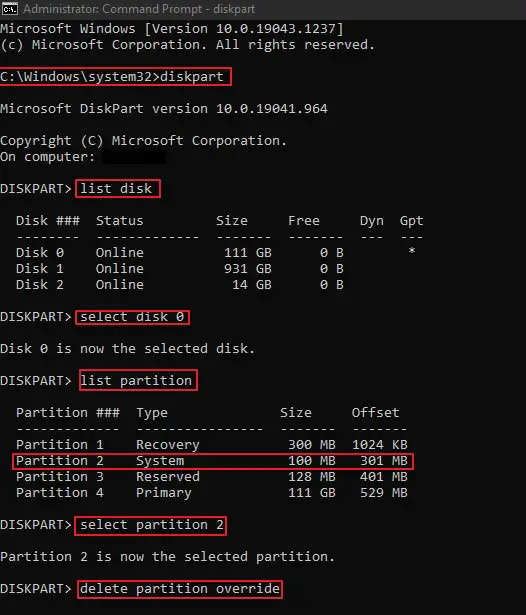
- In the command window, type in “diskpart” and hit Enter.
- Now, type in “list disk” and hit Enter to show a list of all disks.
- Look for the disk with the EFI system partition that you want to delete and note down its given disk number.
- Now type in “select disk #” where you replace # with the disk number. Hit Enter.
- Now type in the “list partition“. This will show all partitions.
- Identify the EFI system partition – it will be listed as system, and it will have a size of about 100 MB.
- Type in “select partition #“, where # is the number of the EFI System Partition.
- Finally, type in “delete partition override” and hit Enter to delete.
- To wipe it, type in “clean” to erase all files on the partition.
From here on out, the EFI system partition is completely wiped, causing all files on this partition to be lost. If you head back into your Disk Management screen, and look to where the EFI system partition was prior to its deletion, you will see 100 MB of unallocated space.
Note: If you were to shut down your computer after deleting the EFI system partition of your current operating system, you may run into boot problems. If this is the case, you will need to either rebuild your EFI system partition manually, restore Windows, or reinstall it.
How to manually create an EFI System Partition if it is missing
You will need a Windows installation media disk to manually recreate the EFI system partition. You can either create one on a DVD or you can create one using a USB flash drive. We recommend using the USB flash drive, as a lot of newer computers may not come with a DVD drive.
- If your computer isn’t already shut down, power it down.
- Insert the USB flash drive into one of your USB ports.
- Power the computer back up, while pressing Shift + F10 to open the command prompt window.
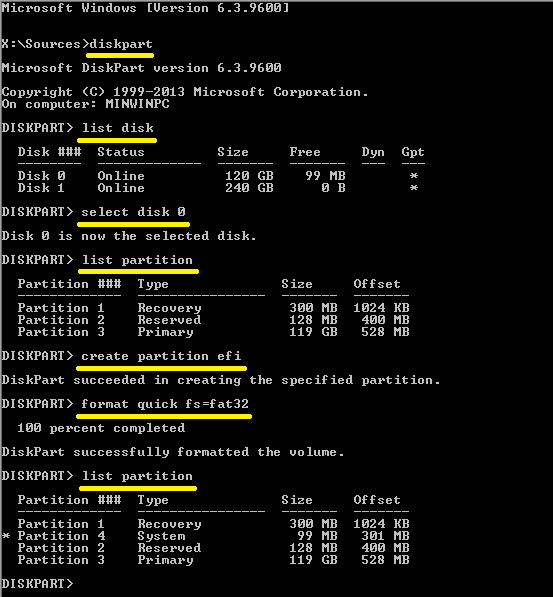
- Type in “diskpart“, hit Enter and wait. It takes DISKPART quite a while to launch.
- Type in “list disk“, hit Enter and view the available disks.
- Type in “select disk #“, where # is the disk where you want to create an EFI system partition.
- Type in “list partition” and press Enter to view the list of partitions available.
- Now type in “select partition #“, where # is a partition which has some unused space.
- Type in “shrink size=500” to shrink that partition by 500 MB. We will use the space freed up this way for the new EFI System Partition.
- Now type in “create partition EFI size=200” to create a sub-partition for your EFI.
- Then use the command line “format quick fs=fat32” to format the EFI partition you just created.
- Now type in “assign letter=S” and press Enter to assign a letter to the partition. (Choose an unused letter)
- Now repeat the “list partition” and “list volume” commands to see where the partition is located and where your operating system is located. Write down their letters.
- Exit diskpart.
To boot, use the command line again and type in “bcdboot %X”\windows /s %S:” where you replace “%X” with the Windows volume letter, and “%S” being the letter of the new EFI system partition you’ve created.
Now you can remove the Windows installation media disk, and restart your computer. Head into your BIOS and in the settings, make sure to set the first boot device to where your Windows operating system is located.